Thermocouple Links
The following links are thermocouple resources
Thermocouples
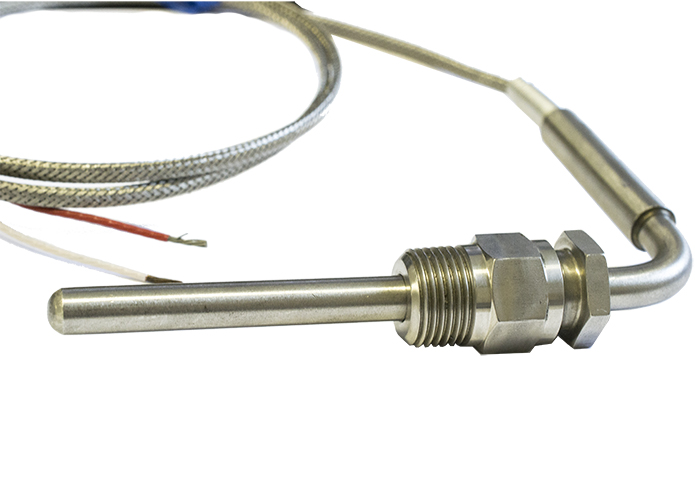
A thermocouple is a sensor for measuring temperature. It consists of two dissimilar metals, joined together at one end.
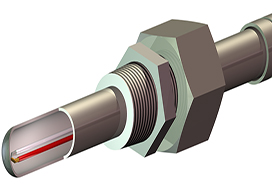
A thermocouple (T/C) is a closed-circuit thermoelectric temperature sensing device consisting of two wires of dissimilar metals joined at both ends. A current is created when the temperature at one end or junction differs from the temperature at the other end. This phenomenon is known as the Seebeck effect, which is the basis for thermocouple temperature measurements.
One end is referred to as the hot junction whereas the other end is referred to as the cold junction. The hot junction measuring element is placed inside a sensor sheath and exposed to the process. The cold junction, or the reference junction, is the termination point outside of the process where the temperature is known and where the voltage is being measured. This cold junction is typically in a transmitter, control system input card or in a signal conditioner.
According to the Seebeck effect, a voltage measured at the cold junction is proportional to the difference in temperature between the hot junction and the cold junction. This voltage may be referred to as the Seebeck voltage, thermoelectric voltage, or thermoelectric EMF. As the temperature rises at the hot junction, the observed voltage at the cold junction also increases non-linearly with the rising temperature. The linearity of the temperature voltage relationship depends on the combination of metals used to make the T/C.
Features Of Industrial Thermocouples -
Industrial thermocouples, in comparison with other thermometers, have the following features:
Precautions for Practical Thermocouple Applications
There are various types of thermocouple, so it is most important to carefully select an appropriate thermocouple for the specific application. In addition, care should be exercised when selecting protection tube, structure of the assembly and installation method in consideration of resistance to heat, pressure, thermal shock, corrosion and vibration. For the best of temperature measurement with thermocouple, overall measuring loop and components should be carefully designed. Although the importance of reference or cold junction is overlooked and often substituted by a simple electric resistor compensation inside the measuring instrument, stability of the reference junction actually controls measurement accuracy.